Disinfectant efficacy testing (DET) is a microbiological test that determines if a disinfectant is effective at removing microorganisms from surfaces and objects. It’s also known as a coupon test. DET is often used in manufacturing areas, laboratories, and other facilities to ensure that cleaning and disinfecting procedures are sufficient to prevent microbial contamination. This is especially important for sterile manufacturing facilities and controlled environments, such as those found in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies.
Disinfectant efficacy testing is a process that assesses the ability of disinfectant products or methods to eliminate microorganisms from surfaces, water, or materials. It involves controlled laboratory experiments where test organisms are exposed to the disinfectant under standardized conditions. The effectiveness of the disinfectant is evaluated by measuring the reduction in microbial populations after exposure. This testing ensures that disinfectant products are capable of achieving specified levels of microbial reduction, thereby helping to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in various settings.
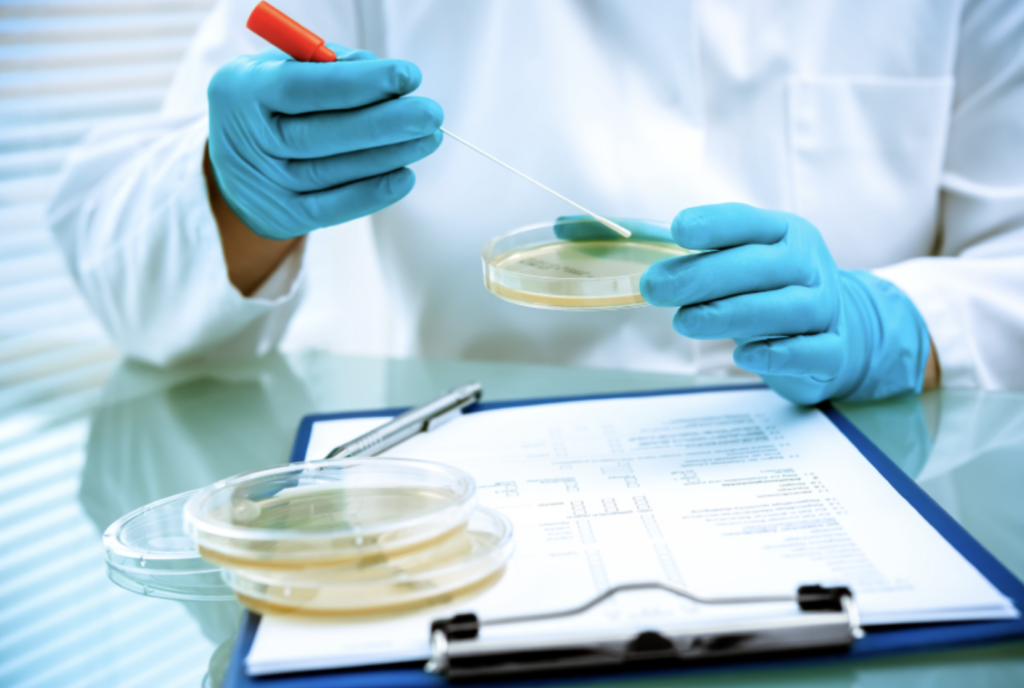

The goal of a disinfectant efficacy study , also known as a coupon test, is to provide evidence that internal cleaning and disinfecting procedures result in a clean and safe manufacturing environment.
What is the FDA test for disinfectants?
FDA requires the following tests for high-level disinfectants per its current guidance: AOAC Use-Dilution Test. AOAC Sporicidal Activity Test. AOAC Fungicidal Activity Test.

Disinfectant validation for pharmaceutical cleanrooms includes many factors, including but not limited to, wet contact time (in vitro and in use) unopened and in-use shelf life, sterility, residues, application methods, storage, disposal, health and safety, audit of manufacturer, as well as the key factor of proving …

Efficiency testing tests the amount of resources required by a program to perform a specific function. In software companies, this term is used to show the effort put in to develop the application and to quantify its user-satisfaction.
What is disinfectant efficacy testing (DET)?
Disinfectant efficacy testing (DET) is microbiological testing to ensure aseptic processing areas are consistently maintained, a validated cleaning and disinfection process is required by U.S. and international regulatory authorities. Pharmaceutical, biotechnology, compounding pharmacy, and medical device companies often have controlled environments that require aseptic processing of components and products.

Disinfectant testing supports infection control in healthcare settings and in the community. Disinfectant testing methods ascertain the activity of antimicrobial agents under specified conditions.
Examples include BS EN 1276 and BS EN 13704 disinfectant standards, which evaluate the bactericidal and sporicidal activity of chemical disinfectants, respectively. These test methods can be used for products within the food, industrial, domestic and institutional industries.