Bioburden is the presence of viable microorganisms on a surface (or complete item), inside a device, or in a portion of liquid, before sterilization. Bioburden can be introduced from the raw materials used in the manufacturing process or through the workforce in the manufacturing environment or during the packaging of end products. With numerous sources of potential contamination, the bioburden of a product can fluctuate between batches hence routine testing is implemented as a part of quality control.

Bioburden testing, or total viable count testing, is the measure of microbial contamination levels on or in a product.
Bioburden can be introduced from the raw materials used in the manufacturing process, or be introduced via the workforce or manufacturing environment. With numerous sources of contamination, the bioburden of a product can fluctuate between batches, so regular, routine testing is advisable.
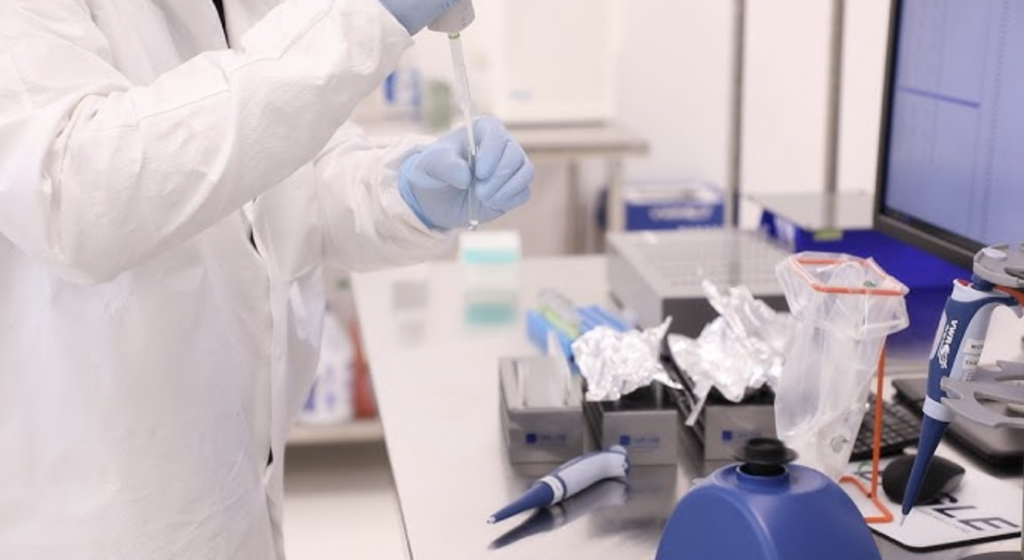


For a sterilisation process to be effective on a newly manufactured pharmaceutical product or medical device, manufacturers must be aware of the number, properties and characteristics of microorganisms that occur in the products naturally or while going through the production process. This is a crucial step prior to setting sterilisation parameters such as dosing, temperature etc. to ensure that the process is effective and the product safe when used.
Bioburden test results may be used to:
- Demonstrate microbial quality control of the manufacturing process through routine monitoring and trending (ISO 11737)
- Determine radiation dose for terminally sterilized product (ISO 11137)
- Investigate root cause of contamination excursions from routine production (Alert and Action levels)
- Test raw and finished product materials for microbiological examination of non-sterile products (USP<61>)
- Methods for the absence of specified or objectionable microorganisms can be developed. These methods not only give total viable counts, but also identify the presence or absence of specified microorganisms, providing complete, robust test results. (USP<62>, USP<60>)
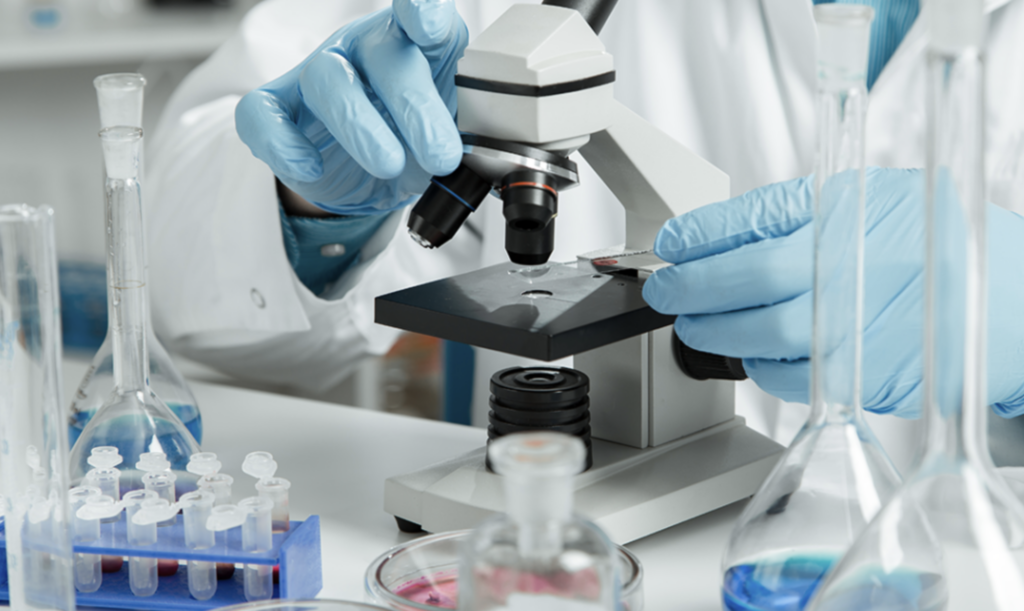
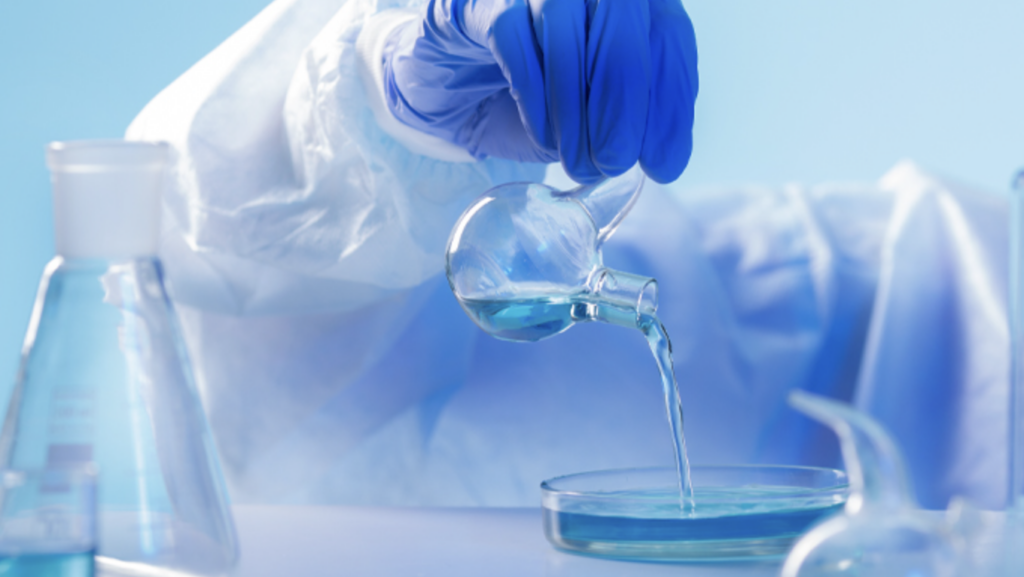



In General Bioburden testing or Microbial testing is a quality control process that detects and quantifies microbial contamination of a product at different stages of production i.e., from initial manufacturing to final distribution. Effective quality control and accurate test results are essential to minimize risks for consumers and are required by regulated production environments. Therefore, bioburden analysis is often included in routine testing to ensure the safety, quality, and regulatory compliance of each manufactured product batch.
Bioburden testing is performed for medical devices, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, water, packaging, raw materials, human tissue, animal tissue, and cosmetics. When standard methods, as described below are followed, it is important to ensure that the testing method does not introduce bacteria into the test sample or kill bacteria in the test sample.