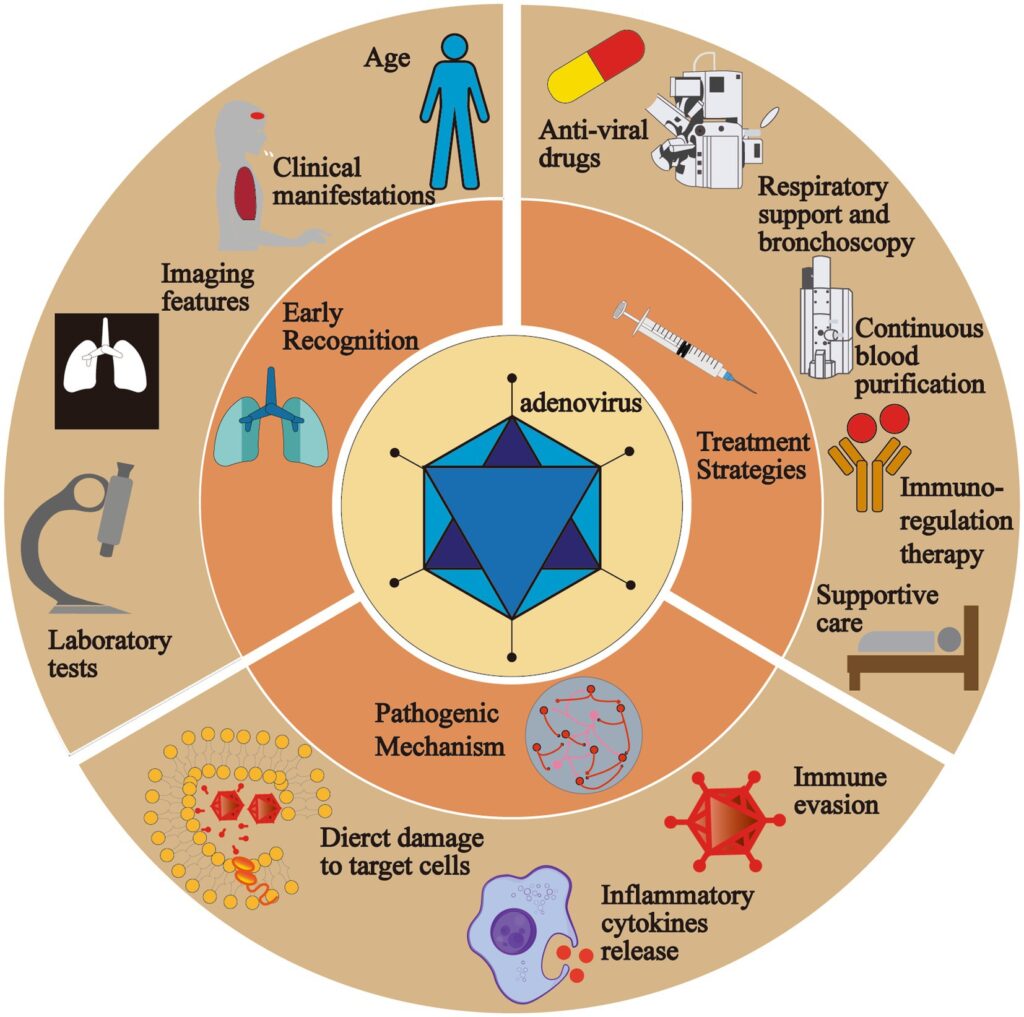
Adenovirus - Symptoms
Adenoviruses are common and typically cause mild cold or flu-like symptoms. Adenoviruses can cause illness in people of all ages any time of year. People with weakened immune systems or existing respiratory or cardiac disease are at higher risk of developing severe illness from adenovirus. Adenoviruses can cause a wide range of signs and symptoms, such as:
- Common cold or flu-like symptoms
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Acute bronchitis (inflammation of the airways of the lungs, sometimes called a "chest cold")
- Pneumonia (infection of the lungs)
- Pink eye (conjunctivitis)
- Acute gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach or intestines causing diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and stomach pain)
- Less common symptoms include: bladder inflammation or infection neurologic disease (conditions that affect the brain and spinal cord)
Adenoviruses are usually spread from an infected person to others through:
Close personal contact, such as: touching or shaking hands. The air, by coughing and sneezing. touching an object or surface with adenoviruses on it, and then touching your mouth, nose, or eyes before washing your hands. Through an infected person’s stool (e.g., during diaper changing). Through the water, such as swimming pools, but this is less common.
How long a person can spread the virus
Sometimes the virus can be shed (released from the body) for a long time after a person recovers from an adenovirus infection, especially among people who have weakened immune systems. This “virus shedding” usually occurs without any symptoms, even though the person can still spread adenovirus to other people.
Prevention
Follow simple steps to protect yourself and others CDC recommends important steps you can take to reduce your risk of getting or spreading a range of common respiratory viruses, including adenovirus. Practice good hygiene (practices that improve cleanliness): Take steps for cleaner air. When you may have a respiratory virus take steps to prevent spread. Frequent handwashing is especially important in childcare settings and healthcare facilities. Maintain proper chlorine levels to prevent outbreaks It is important to keep adequate levels of chlorine in swimming pools to prevent outbreaks of conjunctivitis caused by adenoviruses. CDC’s Healthy Swimming website provides more information on how to maintain healthy and safe swimming environments. Keep Reading: Respiratory Virus Guidance.
Treatment
There are no approved antiviral medicines and no specific treatment for people with adenovirus infection. Most adenovirus infections are mild and may be managed with rest and over-the-counter pain medicines or fever reducers to help relieve symptoms. Always read the label and use medications as directed. If you have concerns, you should speak with your healthcare provider.